2022
Master Cardiovascular System For Mdcat 2022
Master Cardiovascular or Circulatory System
The cardiovascular system is the transport system of the body. It plays a vital role in nutrient distribution and metabolic wastes elimination from the body. It's a very important chapter for the Mdcat exam. Here we are going to start
from the very basic level.
from the very basic level.
Why do multicellular complex organisms need a specialized transport system?
We know that unicellular and simple multicellular organisms have a large surface area exposed to the environment. That is why simple diffusion is efficient for the exchange of nutrients and metabolic wastes consequently there is no need for a specialized transport system. In multicellular complex organisms, the surface area exposed to the environment is very little as compared to the volume of the organism. Simple diffusion is not sufficient because the deeper cells remain deprived of the nutrient and metabolic wastes exchange because they are not exposed to the environment directly. That is why there is a need for a specialized transport system that can supply nutrients to each and every cell of the body and remove the metabolic wastes. This specialized transport system in humans is the cardiovascular system.
1. Mass transport system or blood: For transporting nutrients and gases mass transport system that is blood in humans is acting as a medium in which the nutrients and gases are transported. The blood is water-based mass transport system that is easy to move and can suspend nutrients and gases in it for transportation.
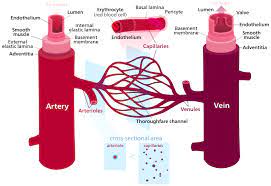
2. Blood vessels: To keep the blood closed there are interconnected tubes known as blood vessels. The blood circulates in these vessels. These blood vessels are spread like a network in all parts of the body in order for the blood to be able for exchanging nutrients and metabolic wastes.
comparison of surface area between unicellular and multicellular organisms
Components of the cardiovascular system: In the human body once the nutrients and gases enter the exchange surfaces(absorption surface in the GIT and respiratory surface in the lungs). These gases and nutrients need to be transported to each and every cell of the body. The cardiovascular system is responsible for all this transportation which consists of the following components:
1. Mass transport system or blood: For transporting nutrients and gases mass transport system that is blood in humans is acting as a medium in which the nutrients and gases are transported. The blood is water-based mass transport system that is easy to move and can suspend nutrients and gases in it for transportation.
2. Blood vessels: To keep the blood closed there are interconnected tubes known as blood vessels. The blood circulates in these vessels. These blood vessels are spread like a network in all parts of the body in order for the blood to be able for exchanging nutrients and metabolic wastes.3. Pumping organ or heart: In order to circulate the blood throughout the body, it needs to be pressurized by a mechanical pumping organ known as the heart. The heart keeps the blood circulating in the blood vessels and thereby transporting nutrients and eliminating the wastes from the body.
In order to keep the blood unidirectional there are valves in the heart and veins. These valves prevent backflow of the blood and keep it circulating unidirectionally.This was an introduction to the cardiovascular system we will try to dive deep into this chapter and master the concepts in the upcoming posts.
In order to keep the blood unidirectional there are valves in the heart and veins. These valves prevent backflow of the blood and keep it circulating unidirectionally.
This was an introduction to the cardiovascular system we will try to dive deep into this chapter and master the concepts in the upcoming posts.








Post a Comment
0 Comments